By: Emily Chittenden
An Introduction to Genetics & the U.S. Genetic Evaluation System
Goal: To breed a better cow that will maximize herd profitability
But how to we achieve that goal?
By breeding genetically superior cows, by focusing on genetic change and progress that accumulates over time (4).
What is genetic change?
Genetic Change = (Accuracy of Selection x Selection intensity x Genetic Variation) / Generation Interval
- Accuracy of Selection: The breeder’s ability to select animals that are truly genetically superior for a given trait.
- Selection Intensity: Dependent upon the proportion and quality of animals kept as breeding stock. The more intense the selection, the more superior a group of animals is compared to the overall population.
- Genetic Variation: The relative difference among animals that are controlled by genetic factors. It is the function of the heritability of a trait.
- Heritability is the proportion of variation in a trait due to genetic factors, measured in numbers ranging from 0 to 1. The higher the number, the more heritable the trait is and the faster genetic progress can be made by selecting for that trait.
- Generation Interval: Average age of a parent when offspring are born.
So how do we speed up genetic progress? GENOMICS!!
Genomics became more widely known starting in 2009-2010 which started the use of genetic testing in that time (4). Genetic testing plays a significant role in speeding up genetic progress by increasing accuracy of selection and decreasing generation interval.
 This brochure gives a more in depth overview of the testing and evaluation system.
This brochure gives a more in depth overview of the testing and evaluation system.
Analyzing an animal’s DNA to indicate which genes are present and may be expressed has increased reliability over traditional evaluation methods.
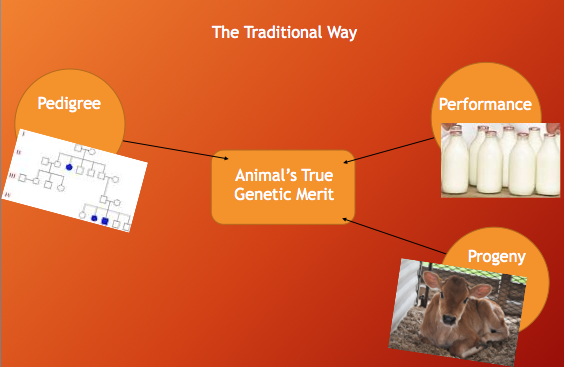
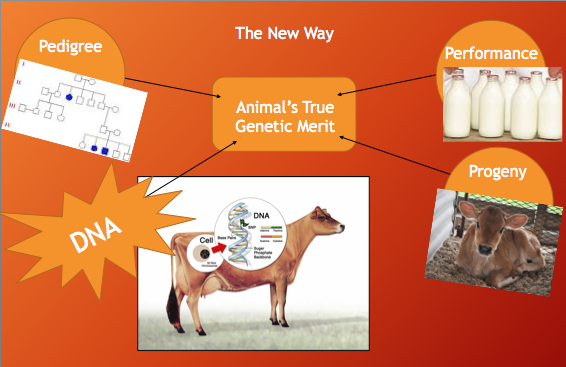
Adding that one extra piece of information has given a faster and more accurate measure of an animal’s genetic merit.
References:
- Dairy Herd Information Association. Mission Goals and Tactics: DHI Equals Management. [Online]. Available from: http://www.dhia.org/DBC/2014%20Mar%20NDHIA-Mission%20goals%20and%20tactics.pdf
- United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. Animal Genomics and Improvement Laboratory Home. [Online]. Available from: https://www.ars.usda.gov/northeast-area/beltsville-md-barc/beltsville-agricultural-research-center/agil/. [Accessed May 8, 2015].
- Holstein Association USA. Classification-Type Evaluation. [Online]. Available from: http://www.holsteinusa.com/programs_services/classification.html. [Accessed May 8, 2015].
- Holstein Foundation. Understanding Genetics and the Sire Summaries. [Online]. Available from: http://www.holsteinfoundation.org/pdf_doc/workbooks/Gen_Sire_WKBK.pdf. [Accessed May 6, 2015].

